From the perspective of principle and practical use, switches in the network are not producers of data packets. The producers of real content are terminals (PCs, mobile phones, and tablets), and the switching equipment is only responsible for the forwarding of data packets. Therefore, as long as the standard 802.3 related PoE switches, such as IEEE802.3ab (gigabit Ethernet standard), IEEE802.1Q (VLAN standard), IEEE802.3z (gigabit Ethernet fiber standard), etc., can be built on the network. General purpose, and compatible with standard equipment. Therefore, it is ridiculous to say that a unified brand will make data compatibility better.
In wireless coverage, PoE switches provide power for wireless APs, and play the role of Layer 2 data exchange and division of different VLANs. Generally, each vendor will comply with standard protocols and be a relatively technically mature device. In actual use, we often encounter users who have switches from multiple vendors at the same time due to capacity expansion or device upgrades, and have never encountered incompatibility issues.
The requirement to use the same brand is as meaningless as requiring the same brand in the network (eg, PC, cell phone, PAD). The emergence of such brand restrictions in wireless construction projects is often caused by users being guided by other vendors for other considerations, thus making it impossible for users to choose more specialized wireless products.
In fact, wireless deployment should return to the essence. It should pay attention to the security, speed, and value of wireless itself. Wireless device manufacturers should also proceed from the nature of customer needs to provide customers with a more professional and secure wireless network.
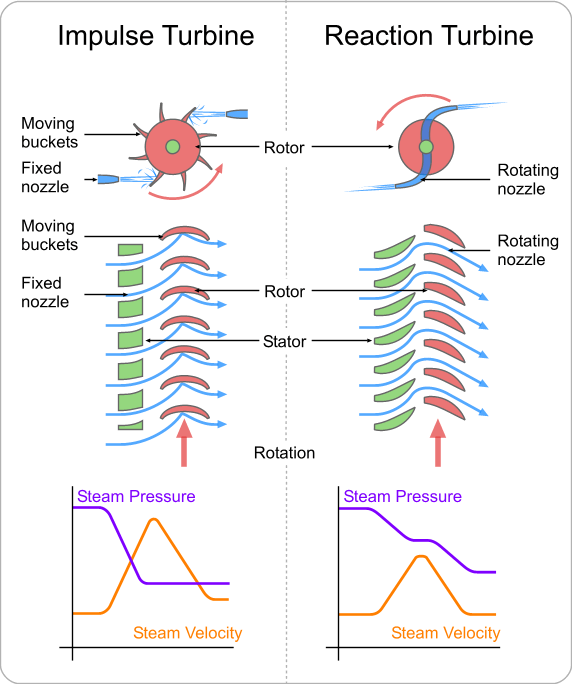
A reaction turbine is a type of Steam Turbine that works on the principle that the rotor spins, as the name suggests, from a reaction force rather than an impact or impulse force.
In a reaction turbine there are no nozzles to direct the steam like in the impulse turbine.
Instead, the blades that project radially from the outer edge of the rotor are shaped and mounted so that the shape between the blades, created by the cross-section, create the shape of a nozzle. These blades are mounted on the revolving part of the rotor and are called the moving blades.
The fixed blades, which are the same shape as the moving blades, are mounted to the outer casing where the rotor revolves and are set to guide the steam into the moving blades. Below is a simple diagram of reaction turbine blades:
Reaction Turbine Principle:
In the case of reaction turbine, the moving blades of a turbine are shaped in such a way that the steam expands and drops in pressure as it passes through them. As a result of pressure decrease in the moving blade, a reaction force will be produced. This force will make the blades to rotate.
Reaction Turbine Working:
A reaction turbine has rows of fixed blades alternating with rows of moving blades. The steam expands first in the stationary or fixed blades where it gains some velocity as it drops in pressure. Then enters the moving blades where its direction of flow is changed thus producing an impulse force on the moving blades. In addition, however, the steam upon passing through the moving blades, again expands and further drops in pressure giving a reaction force to the blades.
This sequence is repeated as the steam passes through additional rows of fixed and moving blades.
Note that the steam pressure drops across both the fixed and the moving blades while the absolute velocity rises in the fixed blades and drops in the moving blades.
The distinguishing feature of the reaction turbine is the fact that the pressure does drop across the moving blades. In other words, there is a pressure difference between the inlet to the moving blades and the outlet from the moving blades.
Special Aspects of Reaction Turbines
- There is a difference in pressure across the moving blades. The steam will, therefore, tend to leak around the periphery of the blades instead of passing through them. Hence the blade clearances as to maintain as minimum as possible.
- Also, due to the pressure drop across the moving blades, an unbalanced thrust will be developed upon the rotor and some arrangement must be made to balance this.
Reaction Steam Turbine
Shandong Qingneng Power Co., Ltd. , https://www.steamturbine.be